Microgreen Cultivation Explained: Process, Technology, and Commercial Scope
- Archit Dosajh
- Jan 3
- 4 min read
Introduction: Why Microgreen Cultivation Demands Industrial Precision
Microgreens have evolved from a niche culinary garnish to a high-value agricultural product supplying hotels, food processors, pharmaceutical companies, and health-focused brands. However, while demand is rising, most microgreen operations struggle with inconsistent yield, microbial contamination, energy inefficiency, and scalability limitations.
Modern microgreen cultivation is no longer a manual farming activity—it is a controlled industrial process. Success depends on precise environmental control, automation, HVAC intelligence, and data-driven decision-making. This is where industrial automation and AI-enabled systems transform microgreen farming from a small-scale activity into a predictable, profitable operation.
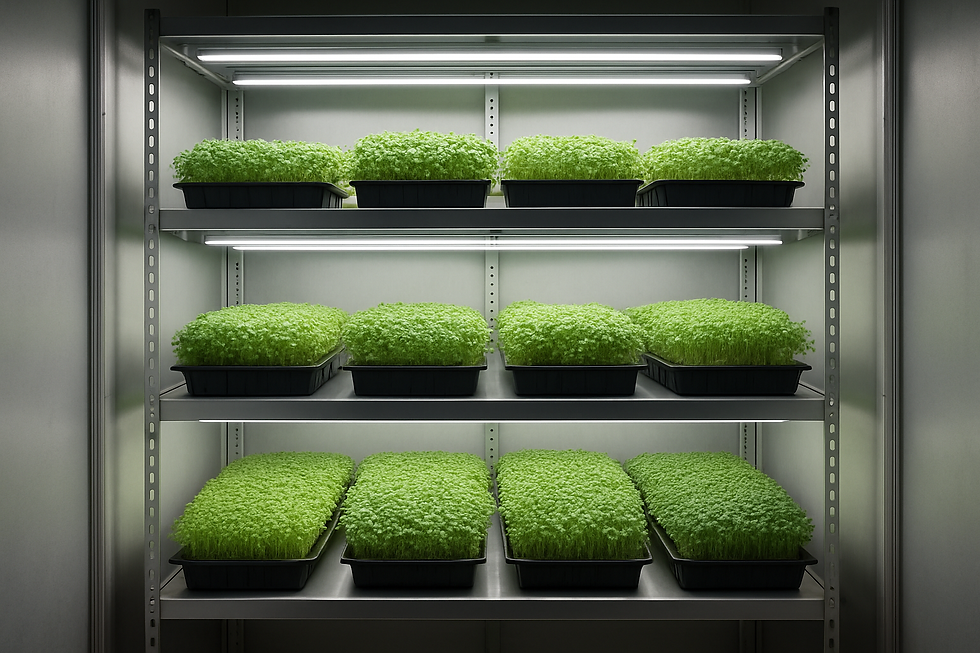

What Is Microgreen Cultivation?
Microgreen cultivation is the controlled growth of young edible greens harvested at an early stage—typically **7 to 14 days after germination**. These crops are valued for:
- High nutrient density
- Short crop cycles
- Low land footprint
- High market price per kilogram
Common commercially grown microgreens include basil, radish, mustard, broccoli, pea shoots, and sunflower.
From an industrial perspective, microgreens are best produced using **indoor controlled environment agriculture (CEA)** systems rather than open or semi-controlled methods.
The Industrial Microgreen Cultivation Process (Step-by-Step)
1. Seed Selection and Preparation
- Use pathogen-tested, food-grade seeds
- Soaking time and moisture levels must be standardized
- Select Non GMO for high quality
2. Sowing and Germination
- Uniform seeding density ensures consistent growth
- Germination often occurs in dark, high-humidity conditions
- Temperature stability is essential to avoid fungal growth
3. Growth Phase (Critical Control Stage)
During this phase, microgreens require:
- Temperature control (18–24°C, crop-dependent)
- Relative humidity control (50–70%)
- CO₂ balance for biomass development
- Uniform LED spectrum and photoperiods
Any fluctuation directly impacts yield quality and shelf life.
4. Harvesting and Post-Harvest Handling
- Harvest timing affects taste, nutrition, and visual appeal
- Rapid cooling and hygienic handling are mandatory
- Cold storage integration is critical to preserve freshness
Technology Stack Behind Modern Microgreen Farms
Controlled Environment Infrastructure
Commercial microgreen cultivation relies on:
- Insulated grow chambers or cold rooms
- Multi-tier vertical racks
- Hygienic flooring
- air circulation design
These systems closely resemble industrial cold rooms and clean processing environments rather than traditional farms.
HVAC Intelligence and Environmental Control
HVAC is the backbone of scalable microgreen cultivation.
Key HVAC requirements include:
- Precise temperature modulation
- Dehumidification to prevent mold
- Airflow balancing across racks
- Energy-efficient heat recovery
Without intelligent HVAC systems, microgreen farms face:
- Uneven growth
- High rejection rates
- Rising energy bills
This is where AI-driven HVAC optimization delivers measurable ROI.
Automation and Sensor Networks
Modern microgreen farms integrate:
- Temperature and humidity sensors
- CO₂ and airflow sensors
- Automated irrigation and misting
- PLC(programmable logic controller) panel
Automation eliminates manual errors and ensures repeatability—critical for B2B supply contracts.
Commercial Scope and Business Viability
Why Microgreens Are Commercially Attractive
From a business perspective, microgreens offer:
- Fast production cycles (weekly harvests)
- Predictable output with automation
- Premium pricing in urban markets
- Low logistics risk with local production
However, profitability depends on process control, not just crop selection.
Industrial Use-Cases
Microgreen cultivation systems are increasingly adopted by:
- Food processing plants supplying ready-to-eat products
- Pharmaceutical and nutraceutical manufacturers
- Hospitality supply chains
- Health Conscious People
In these environments, standardization, traceability, and uptime matter more than farming intuition.
Operational Challenges Without Automation
Many microgreen businesses fail to scale due to:
- Manual climate adjustments
- Inconsistent HVAC performance
- Unplanned downtime
- High labor dependency
- Lack of predictive insights
These challenges mirror problems seen in manufacturing plants before automation adoption.
How Enables Intelligent Microgreen Cultivation
Precite.ai applies industrial automation principles to agricultural environments.
Key Capabilities:
- AI-Driven Climate Control
Adaptive algorithms maintain optimal temperature and humidity with minimal energy usage.
- Predictive Maintenance for HVAC & Chillers
Detects early signs of equipment failure, preventing crop loss.
- Centralized Monitoring Dashboards
Real-time visibility across multiple grow chambers and locations.
- Energy Optimization
Reduces HVAC and lighting costs through load balancing and demand-based control.
Precite.ai’s approach treats microgreen cultivation as a process industry, not a hobby—ensuring consistency, compliance, and commercial viability.
---
ROI of Automation in Microgreen Cultivation
Automation-driven microgreen farms typically achieve:
- Reduced crop loss from environmental deviations
- Lower energy consumption per kilogram produced
- Higher batch consistency
- Faster scalability without proportional labor increase
These benefits directly align with CFO-level decision metrics rather than agricultural experimentation.
FAQs
What is the ideal environment for microgreen cultivation?
A controlled indoor environment with stable temperature, humidity, airflow, and lighting delivers the most consistent results.
Can microgreen cultivation be fully automated?
Yes. From irrigation to HVAC and monitoring, microgreen farms can be largely automated using industrial control systems.
Is HVAC really critical for microgreens?
Absolutely. HVAC stability directly affects yield quality, food safety, and operational costs.
What industries benefit most from automated microgreen farming?
Entrepreneur, Food processing, hospitality supply chains, nutraceuticals, and export-focused agri-businesses gain the most value.
How scalable is microgreen cultivation?
With modular automation and AI-driven control, microgreen farms can scale from pilot setups to industrial facilities.
Conclusion: Microgreens as an Industrial Opportunity
Microgreen cultivation is no longer just an agricultural trend—it is an **industrial growth opportunity** when supported by automation, HVAC intelligence, and data-driven control.
Organizations that treat microgreens as a controlled manufacturing process gain:
- Predictable output
- Lower risk
- Higher margins
- Faster scalability
For businesses looking to enter or expand microgreen production, investing in intelligent infrastructure from the start is the difference between experimentation and long-term profitability.
Ready to industrialize your microgreen operation?













Comments